Hostilities in the Gaza Strip and Israel | Flash Update #60
Key points
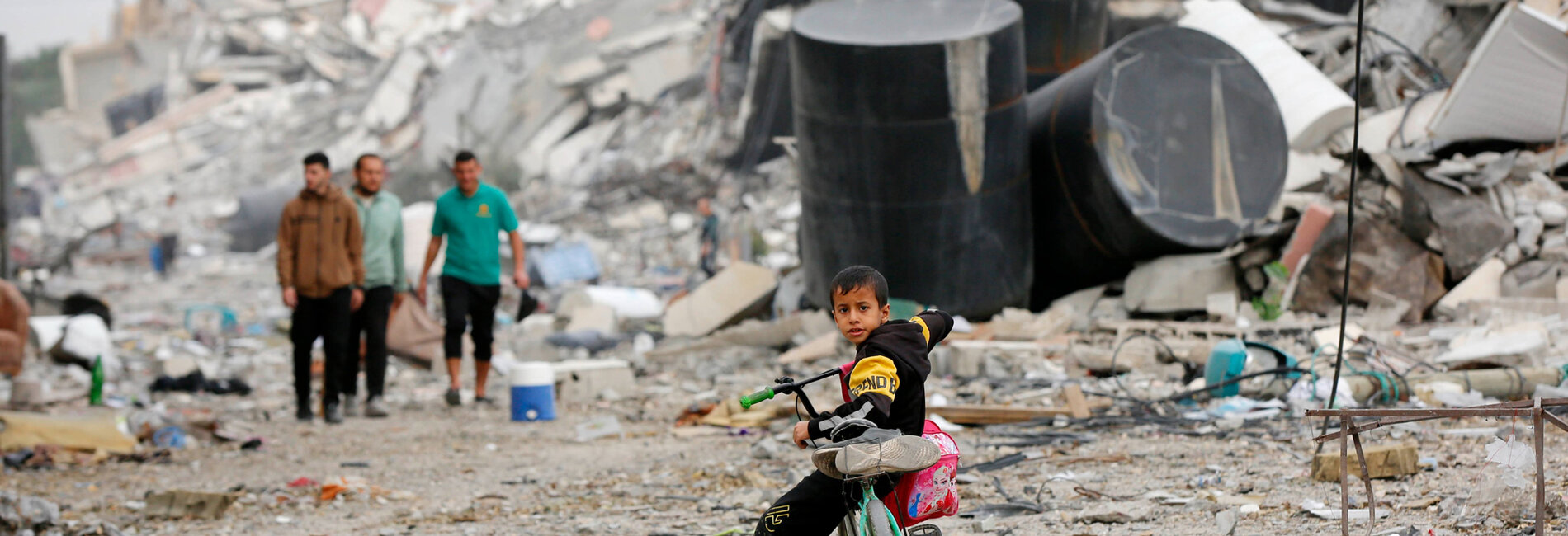
- Israeli bombardments from air, land, and sea across Gaza have significantly intensified since 4 December afternoon, alongside intense fighting between Israeli forces and Palestinian armed groups, in particular in the eastern parts of Gaza city, Jabalia refugee camp, and areas east of Khan Younis. Rocket firing by Palestinian armed groups to Israel also increased.
- On 5 December, the Emergency Relief Coordinator, Martin Griffiths stated: “Nowhere is safe in Gaza. Not hospital, not shelters, not refugee camps. No one is safe. Not children. Not health workers. Not humanitarians. Such blatant disregard for basic humanity must stop. The fighting must stop.”
- According to the Gaza Ministry of Health (MoH), since the resumption of hostilities on 1 December and until 5 December 18:00, at least 1,207 Palestinians were killed, 70 per cent of whom were children and women. On 5 December, the UN Human Rights Office stated that “the pattern of attacks that target or impact on civilian infrastructure raises serious concerns about Israel’s compliance with international humanitarian law and significantly raises the risk of atrocity crimes.”
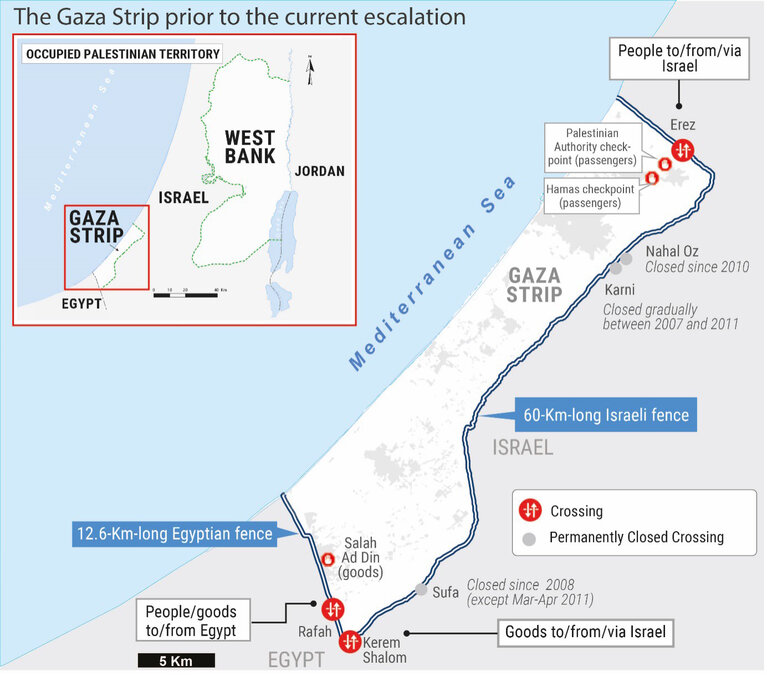
- On 5 December, dozens of aid trucks carrying humanitarian supplies and fuel entered from Egypt into Gaza; however, as of 23:00, figures were not available. The ability of the UN to receive incoming loads of aid has been significantly impaired over the past three days by several factors. These include a shortage of trucks within Gaza, with some being stranded in the Middle Area, which has been severed from the south; the telecommunications blackout on 4 December; and the increasing number of staff who were unable to report to the Rafah crossing due to the hostilities. On 4 December, the Deputy Special Coordinator and Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for the Occupied Palestinian Territory, Lynn Hastings stated that “the use of only the Rafah crossing - meant for pedestrians - to bring in trucks of goods does not work.”
- On 5 December, for the third consecutive day, Rafah was the only governorate in Gaza where limited aid distributions took place. In the adjacent Khan Younis governorate, aid distribution largely stopped due to the intensity of hostilities. The Middle Area was largely disconnected from the south, following Israeli forces’ restrictions of movement along the main roads. Access from the south to areas north of Wadi Gaza (hereafter: the north) came to a halt on 1 December, with the resumption of hostilities.
- Since 3 December, tens of thousands of IDPs have arrived in Rafah, presumably from the areas across the Khan Younis governorate. As shelters in Rafah city have exceeded their capacity by far, most newly arriving IDPs have settled in the streets and in empty spaces across the city. UNRWA has distributed hundreds of tents, which have been erected in two separate sites alongside hundreds of makeshift shelters.
- On 3 December, the Israeli military designated an area covering about 20 per cent of Khan Younis city for immediate evacuation. Similar evacuations orders were issued in previous days for a large area east of Khan Younis. Together, these areas in Khan Younis governorate encompass about 22 per cent of the Gaza Strip. Prior to the hostilities, they were home to about 381,000 people; an additional 245,000 IDPs were staying there in 71 shelters; alongside others staying with host families. The Israeli military instructed residents to move to two areas in Rafah and to Al Fakhouri in eastern Khan Younis,
- Under international humanitarian law, parties to a conflict must take all feasible precautions to avoid, and in any event to minimize, civilian harm. This can entail evacuating civilians or giving effective advance warning of attacks, which provides civilians enough time to leave, as well as a safe route and place to go. All possible measures must be adopted to ensure that those civilians displaced can afford satisfactory conditions of safety, shelter, nutrition, and hygiene and ensure that family members are not separated. Civilians choosing to stay in areas designated for evacuation do not lose their protection.
- On 4 December, the World Health Organization (WHO), expressed concern that the intensification of hostilities in and around Khan Younis “are likely to cut thousands off from health care – especially from accessing Nasser Medical Complex and European Gaza Hospital, the two main hospitals in southern Gaza – as the number of wounded and sick increases.”
- On 5 December, the World Food Programme (WFP) stated that “the resumption of hostilities in Gaza will only intensify the catastrophic hunger crisis that already threatens to overwhelm the civilian population.” The statement indicated that “the renewed fighting makes the distribution of aid almost impossible and endangers the lives of humanitarian workers.”
Hostilities and casualties (Gaza Strip)
- The following are among the deadliest incidents reported since the afternoon of 4 December, involving the hitting of residential buildings:
- On 4 December, at about 14:40, seven people, including two girls, were reportedly killed in Deir al -Balah;
- On 4 December, at about 15:40, seven people were reportedly killed in Khan Yunis;
- On 5 December, at about 07:30, 15 people were reportedly killed in Jabalia;
- On 5 December, at about 8:50, ten people were reportedly killed in the new camp in Nuseirat, Middle Area.
- On 3 December, an UNRWA school in Khan Younis sheltering nearly 3,800 IDPs was hit following a strike nearby, killing four IDPs and injuring seven, while another UNRWA school in Deir Al Balah, sheltering about 6,170, sustained damage. Since 7 October, an estimated 222 IDPs sheltering in UNRWA shelters have been killed and another 911 injured.
- According to the Ministry of Health (MoH) in Gaza, between 7 October and 5 December, at least 16,248 Palestinians were killed in Gaza, about 70 per cent of whom are said to be women and children. Many more are missing, presumably under the rubble, awaiting rescue or recovery.
- Overall, 85 Israeli soldiers have been killed in Gaza since the start of the Israeli ground operations, according to official Israeli sources.
Displacement (Gaza Strip)
- On 1 December, the Israeli military issued a detailed online map, where the Gaza Strip is divided into hundreds of small areas. Reportedly, the map is intended to facilitate orders to evacuate people to specific areas ahead of their targeting. On the following two days, various areas, encompassing about 28 per cent of the Gaza Strip, were marked for evacuation. The ability of residents to access this information is impaired by the recurrent interruptions in telecommunications and the lack of electricity to charge electronic devices.
- According to UNRWA, nearly 1.9 million people in Gaza, or nearly 85 per cent of the population, are estimated to be internally displaced (IDPs) as of 3 December. Nearly 1.2 million of these IDPs are registered in 156 UNRWA facilities across Gaza, of whom about one million are registered in 99 UNRWA shelters in the south. Another 191,000 IDPs are estimated to be staying in 124 public schools and hospitals, as well as in other venues such as wedding halls, offices, and community centres. The rest are hosted by families or out in on the open, near shelters. However, obtaining an accurate count is challenging, especially given difficulties in tracking IDPs staying with host families, movement of IDPs following evacuation orders since 1 December, and access restrictions.
- Due to the overcrowding and poor sanitary conditions at UNRWA shelters in the south, there have been significant increases in some communicable diseases and conditions such as diarrhea, acute respiratory infections, skin infections and hygiene-related conditions like lice. There are also initial reports of disease outbreaks, including potentially Hepatitis A.
- Concerns have been raised about vulnerable groups of people who are struggling with difficult shelter conditions. This includes people with disabilities;women who are pregnant, have recently given birth, or are breastfeeding; people who are recovering from injuries or surgeries; and those with compromised immune systems.
Electricity
- Since 11 October, the Gaza Strip has been under an electricity blackout, after the Israeli authorities cut off the electricity supply, and fuel reserves for Gaza’s sole power plant depleted. Depending on the availability of fuel, electricity is produced by generators, as well as by solar panels. For more information on electricity supply to the Gaza strip, please see this dashboard.
- Health care, including attacks (Gaza Strip)
- Between 4 and 5 December, two series of airstrikes hit the vicinity of Kamal Adwan Hospital in Jabalia, resulting in an unknown number of casualties; ground battles between Israeli forces and Palestinian armed groups have been ongoing nearby. Over 10,000 IDPs have been sheltering inside and around the hospital and are unable to leave due to the fighting. Media reports indicate that corpses have been accumulating inside the facility without possibility of burial.
- On 5 December, at about 11:30, a number of people were injured, including a paramedic, when two Palestine Red Crescent Society (PRCS) ambulances transporting people injured and killed south of Deir al Balah were hit.
- Hospitals in the south are barely able to cope with the influx of injuries including two hospitals which Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) supports – Al Aqsa and An Nasser. This challenge is compounded the MSF’s suspension of support to two medical clinics located in areas under evacuation orders. MSF reported that, on 3 and 4 December, more than 100 fatalities and 400 injuries arrived at Al Aqsa hospital. To address this surge, a temporary wound dressing unit has been set up to provide wound management to patients with chronic wounds or injuries.
- The 12 hospitals in the south are partially functional. At present, the bed capacity across Gaza is 1,400, down from 3,500 beds prior to the hostilities. This decline comes amid a surge in those seeking treatment. Only one of the currently functional hospitals has the capacity to treat critical trauma cases or perform complex surgery, according to WHO.
Water and sanitation (Gaza Strip)
- Grave concerns about waterborne diseases due to water consumption from unsafe sources persist, particularly in the north where the water desalination plant and the pipeline from Israel was shut down. There has been almost no improvement in the access of residents in the north to water for drinking and domestic purposes for weeks.
- UNRWA continues to operate nine water wells pumping about 10,000 cubic metres a day to provide potable and domestic water supply in shelters across Gaza. Potable water trucking operations to the shelters in Rafah and Khan Younis areas continue despite the dangerous conditions. Additionally, shelters in Rafah started receiving potable water through tankers from the Coastal Municipalities Water Utility.
- Solid waste collection from the camps, shelters and transfer to landfills continued in the Middle Area, Khan Younis and Rafah. About 45 loadings were transferred to temporary dumping sites on 3 December. There is an urgent need for additional sanitation trucks and vehicles.
Hostilities and casualties (Israel)
- The indiscriminate rocket fire by Palestinian armed groups from Gaza towards Israel intensified on 5 December; no fatalities were reported. Over 1,200 Israelis and foreign nationals have been killed in Israel, according to the Israeli authorities, the vast majority on 7 October.
- During the humanitarian pause (24-30 November), 86 Israeli and 24 foreign national hostages were released. It is estimated that about 138 people remain captive in Gaza, including Israelis and foreign nationals, according to Israeli sources. Before the pause, four civilian hostages had been released by Hamas, one Israeli soldier had been rescued by Israeli forces, and three bodies of hostages had reportedly been retrieved by Israeli forces.
Violence and casualties (in and around the West Bank)
- On 4 December, two Palestinian men were shot and killed by Israeli forces in Sa'ir (Hebron) next to their homes; no confrontations were reported at the time of the shooting. On 5 December, Israeli forces shot in the head and killed a Palestinian man after breaking into his apartment in Qalandiya refugee camp (Jerusalem) during a search and arrest operation.
- Since 7 October, 249 Palestinians, including 65 children, have been killed in the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. Additionally, two Palestinians from the West Bank were killed while carrying out an attack in Israel on 30 November. Of those killed in the West Bank, 239 have been killed by Israeli forces, eight by Israeli settlers and another two have been killed either by forces or settlers. The eight-week toll represents more than half of all Palestinians killed in the West Bank this year. Already, 2023 is the deadliest year for Palestinians in the West Bank since OCHA began recording casualties in 2005.
- Since 7 October, four Israelis, including three members of Israeli forces, have been killed in attacks by Palestinians in the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. An additional four were killed in West Jerusalem in a Palestinian attack (one of whom was killed by Israeli forces who misidentified him).
- Two-thirds of the Palestinian fatalities in the West Bank since 7 October have occurred during search-and-arrest and other operations carried out by Israeli forces, including some – mainly in Jenin and Tulkarm governorates – involving exchanges of fire with Palestinians. More than half of the fatalities were reported in operations that did not involve armed clashes.
- Since 7 October, Israeli forces have injured 3,325 Palestinians, including at least 528 children; 45 per cent of them in the context of demonstrations and 46 per cent in the context of search-and-arrest and other operations. An additional 84 Palestinians have been injured by settlers and 18 others either by Israeli forces or settlers. Some 33 per cent of those injuries have been caused with live ammunition, compared with 9 per cent in the first nine months of 2023.
Settler Violence
- On 4 December, armed assailants who are known by Palestinian residents to be settlers but were wearing Israeli military uniforms, raided the community of Khirbet Zanuta (Hebron); they demolished one residential structure, two animal structures, and partially destroyed the walls of a classroom of the school in the community.
- Since 7 October, OCHA has recorded 318 settler attacks against Palestinians, resulting in Palestinian casualties (35 incidents), damage to Palestinian-owned property (241 incidents), or both casualties and damage to property (42 incidents). The weekly average of such incidents during this period stands at 39, compared with 21 incidents between 1 January and 6 October 2023. However, the number of incidents since 7 October has gradually declined from 80 incidents in the first week (7-14 October) to 18 incidents in the last (27 November - 3 December). One-third of these incidents included firearms, including shootings and threats of shootings. In nearly half of all recorded incidents, Israeli forces were either accompanying or reportedly seen as supporting the attackers.
Displacement (West Bank)
- Since 7 October, at least 143 Palestinian households comprising 1,014 people, including 388 children, have been displaced amid settler violence and access restrictions. The displaced households are from 15 herding/Bedouin communities.
- On 2 December, Israeli forces sealed off on punitive grounds the homes of two brothers from Sur Bahir, in East Jerusalem, accused of killing three Israelis in West Jerusalem, on 30 November. As a result, two households comprising of five people, including two women and three children, were displaced.
- Additionally, 283 Palestinians, including 149 children, have been displaced since 7 October following demolitions in Area C and East Jerusalem, due to lack of Israeli issued building-permits; and 63 Palestinians, including 31 children, have been displaced following punitive demolitions.
Funding
- As of 4 December, Member States have disbursed US$377.1 million against the updated Flash Appeal launched by the UN and its partners to implement its response plan in support of 2.2 million people in the Gaza Strip and 500,000 in the West Bank. This constitutes about 31 per cent of the $1.2 billion requested. Private donations are collected through the Humanitarian Fund.
HUMANITARIAN NEEDS AND RESPONSES: 27 November – 3 December
Health
During the reporting period, Cluster partners have carried out the following activities across Gaza:
- Some 150 mobile medical teams provided primary health-care services to IDPs. Partners are working to increase the number of mobile teams to cover more shelters;
- About 40,000 primary healthcare consultations were conducted daily through fixed and mobile services, including shelters in the north;
- Some 600 individual clean delivery kits were distributed to 13 shelters north of Gaza;
- Some 10,000 hygiene kits were distributed to IDPs in shelters in the north;
- A daily average of 500 post-natal care and high-risk pregnancy consultations were conducted;
- Cash assistance was provided to 455 patients with non-communicable diseases in the north to procure medications;
- Mental health and psycho-social support services were delivered to about 11,000 people through mobile health teams;
During the humanitarian pause, coordination of movement of health partners and medical supplies, especially to the north was complex. Insecurity in Gaza has forced partners to stop operations and/or prevented them from reaching certain locations, especially the north. Lack of fuel, and other essential supplies continues to pose major challenges for partners’ response. Displacement of partners, their staff and families also continue to affect operational capacity. Overcrowding in the shelters is complicating the delivery of health services and increasing the risk of communicable diseases, including outbreak-prone diseases.
Protection
Risk education, conflict preparedness, explosive ordinance assessment and ultimately mine disposal remain key priorities. During the reporting period, cluster partners dessiminated text messages on Explosive Ordnance Risk Education (EORE) and Conflict Preparedness( CPP) to more than 1 million people. More than 11,100 children and adults IDPs in shelters participated in 227 EORE sessions, and 900 EORE/ CPP posters, including safety messages were distributed by Humanity and Inclusion (HI), an international NGO, in the southern governorates. The United Nations Mine Service (UNMAS) delivered two short training for trainers' sessions on EORE to 100 UNRWA protection focal points in Khan Younis and Rafah – who will then train people in UNRWAs southern shelters. NPAs Social media campaign reached over 2 million people (52 per cent in Gaza, 48 per cent in the West Bank) and another campaign organized by UNMAS/ Mine Action Group (MAG) reached 1.2 million in Gaza and 980k in WB). A scale up on all fronts is urgently needed. Access constraints and communication challenges as well as shortage of material information supplies suitable for different groups including children remain challenging.
An explosive threat assessment (ETA) was conducted at an UNRWA Health Centre in Al Bureij. The centre was struck by several tank rounds impacting the southern and southwest walls, causing extensive damage inside.. A second ETA was conducted at two schools/shelters in Nuseirat that were hit twice in November.
UNMAS accompanied aid missions to Gaza city and conducted an ETA at UNRWA Field Office in Gaza. The compound perimeter walls were damaged by airstrikes hitting surrounding areas. There was also fire damage and evidence of looting. Much of the damage is assessed to be quickly repairable.
‘Humanity and Inclusion’ teams assessed 98 UN and non-UN shelters in the south and conducted 67 recreational activities providing psychosocial support to more than 28,800 people. ‘Stars of Hope,’ an INGO, issued position papers on the complex impact and challenges facing persons with disabilities in Gaza.
UNICEF is signing an agreement with SOS Children’s Village International for the referral of unaccompanied and separated children to specialized services. Since 7 October, SOS has been hosting 75 children, and it has capacity to host another 15 children. Once non-food items are delivered, hosting capacity will increase to an additional 40 places for children 3 years and above. UNRWA and UNICEF are preparing a referral mechanism for unaccompanied and separated children. UNRWA Protection is also coordinating with Terres des Hommes, another NGO, on the provision of psychological first aid, individual counselling and referral support to the Gaza Community Mental Health Programme, including provision of medications for UNRWA’s shelters.
Food security
Food assistance response during the reporting period has included the following:
- • UNRWA distributed flour to 23,384 families in the south. Flour continued to be prioritised for distribution in the north as part of the humanitarian convoys that took place during the ongoing humanitarian pause.
- • UN agencies and the Palestine Red Crescent Society provided ready-to-eat food, including 7.6 metric tons of high-energy biscuits distributed by WFP, covering the minimal daily food intake for 23,616 people at UNRWA shelters in Jabalia.
- • Since the start of the humanitarian pause, WFP reached 121,000 people in shelters and host communities with bread, food parcels, and e-vouchers. WFP is partnering with Global Communities to distribute food parcels to IDPs in host communities. WFP also started distributing hot meals in coordination with local partners, reaching around 6,000 people over two days.
- • Secure Islamique France distributed baskets to 3,000 people in Khan Younis.
- • ANERA continues buying fresh meat and fish from poor farmers, cooking and distributing hot meals (meat and rice or fish and rice), reaching 460,000 people.
- • PUI distributed food baskets to 3,000 IDPs in Khan Younis and the Middle area in public shelters, as well as to cancer patients and their families in Al Salam Hospital. PARC distributed 500 vegetable baskets to IDPs in host communities in Khan Younis and the Middle Area.
- • IHH is distributing 5,000 cooked meals and 500 daily bread bundles on a daily basis and plans to distribute ready-to-eat (RTE) food to 30,000 families staying in UN and non-UN shelters in different locations.
- • Oxfam, in partnership with ESDC, is distributing fresh vegetable parcels and food. The parcels include tomatoes, eggplant, and cucumbers, which could be changed according to the availability of vegetables.
- • In partnership with PARC, UPA continues distributing fresh vegetable baskets, reaching around 5,000 people.
- • PARC will distribute 251 E-Vouchers through FSS's emergency response and 231 E-Vouchers.
- • Middle East Children's Alliance targets providing food parcels to 20,000 people staying with host families in the Khan Younis area.
Nutrition
The Nutrition cluster was officially activated on 9 November. UNICEF is leading the cluster, which currently has 27 partners. The cluster monitors the nutrition situation in Gaza and supports partners to scale up aid for mothers and children through preventive and curative interventions.
During the reporting period, the following nutrition responses were undertaken:
- UNICEF delivered anaemia treatment for more than 33,300 pregnant and breastfeeding women; High Energy Biscuits for 15,000 children (6-23 months); micronutrients supplementation for 16,000 children (24-59 months); and 2,400 pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Vitamin A and Zink supplementation were provided to more than 260,000 children (6-59 months).
- WFP delivered 8,420 cartons of High Energy Biscuits that benefitted 105,830 people in need.
Shelter and Non-Food Items (NFI)
During the reporting period, it is observed that there is still a significant shortage of basic shelter materials, which includes supplying tents, tarpaulines, and plastic sheeting for protection during rainy days, particularly for people living outside the shelters. Shelter partners distributed the following items to IDPs:
- 16,500 winter clothing kits.
- 3,800 kitchen kits.
- 7,500 blankets and mattresses.
- 4,400 washing kits.
- 300 sealing-off kits for winterization.
Due to limited supplies, shelter partners were only able to cover less than 10 per cent of the overall Shelter/NFIs needs. There is still a major gap in shelter winterization materials and essential NFIs, including sealing off kits for damaged houses; a high shortage in bedding sets, including mattresses and blankets to cover the needs of the IDPs in various settings, including UNRWA shelters, as well as winterized tents to protect homeless IDPs from harsh weather condition.
Education
Since 7 October, nine Education Cluster partners have reached 50,726 students and teachers. The main deliverables included emergency learning and recreational supplies (26,833 people reached), psychosocial support (31,318 reached), and recreational activities (49,726 reached). The response has been focusing on Khan Younis, Rafah, and the Middle Area governorates, as North Gaza and Gaza governorates are inaccessible.
Multi-Purpose Cash assistance (MPCA)
Since the beginning of the hostilities, 66,870 households (including roughly 449,000 people) received Emergency MPCA. Cash out rates across the response stand at 70-75 per cent but have been declining slightly over the past few days. While distribution is delivered across the Gaza strip, the vast majority is now concentrated in the south.
Formal market actors, such as supermarkets and retailers are largely depleted and facing major challenges in re-stocking and operating. However, informal markets, such as vendors, minimarts, carts and stalls, reportedly turned into the main source for goods. Information is still unclear on whether shops and markets actors were able to restock during the pause.
Post distribution monitoring data from recipients of cash assistance point to food, water, medicines, hygiene products, and clothing as the top expenditures reported. About 81 per cent of respondents reported that unrestricted cash helped them accessing needed goods and services, either fully or partially. Over 95 per cent reported unrestricted cash as their preference for future assistance.
Logistics
The Logistics Cluster developed and disseminated a new online reporting form to collect information regarding incoming supplies as well as the current stock levels in Egypt and other countries. The form was shared with 34 organisations that are part of the Logistics Cluster and other Clusters and is an ongoing project to be updated on a weekly basis.
On 22 November, 21 mobile storage units (MSUs) arrived in Al Arish, Egypt. The MSUs will be installed, in Egypt to augment the Egyptian Red Crescent’s (ERC) warehousing capacity, and 11 will be delivered to Gaza to expand the storage capacity in key locations. An additional three MSUs were already delivered to Gaza and are in the process of being installed. The latter MSUs will provide an additional 960 m2 of storage capacity. To further support partners inside Gaza, an International NGO will support with providing access to their storage capacity through the Logistics Cluster to receive I/NGOs’ cargo on behalf of the wider humanitarian community.
Emergency Telecommunications
The Emergency Telecommunications Cluster (ETC) continues to coordinate a collective approach among partners for the importation of telecommunications equipment into Gaza. On 3 December, the ETC team, UNDSS, the NGO Help, and UNOCHA met with the Israeli Coordinator of Government Activities in the Territories (COGAT) to discuss the list of technical equipment and solutions submitted for importation into Gaza— to install an independent connectivity and security communications services for humanitarian responders. Following the feedback received from COGAT, the team is developing a revised detailed proposal containing the consolidated description of all equipment and solutions required to operate in Gaza. On 3 December, COGAT also authorized the team to purchase 20 satellite phones from a local service provider and import into Gaza for use by humanitarian responders. The ETC alerted COGAT of the ongoing limited internet connectivity for humanitarian responders, while UNOCHA raised the issue of limited fuel access for Mobile Network Operators—to power telecommunications towers.
Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
N/A
Protection against sexual abuse and exploitation (PSEA) remains a cross-cutting priority for all clusters. The SAWA helpline, reachable at 121 and through WhatsApp at +972 59-4040121 (East Jerusalem at 1-800-500-121), operates 24/7. This toll-free number is widely disseminated across all areas of intervention to report cases of SEA and to facilitate emergency counselling and referrals for affected communities to access life-saving services. The PSEA Network monitors calls daily and will increase the number of counsellors if necessary.
* Asterisks indicate that a figure, sentence, or section has been rectified, added, or retracted after the initial publication of this update.